Payroll is one of the most vital functions in any organisation. In the United States, payroll management involves more than just paying salaries; it ensures accurate calculation of wages, lawful tax deductions, and compliance with several federal and state regulations. For HR and finance professionals in India aiming to work with US-based clients or multinational companies, understanding the US payroll process is a major career advantage.
With several years of experience in US payroll management, I’ve handled end-to-end payroll processing, compliance with federal and state regulations, and system implementations across multiple industries. My work has reinforced how critical accuracy, timeliness, and compliance are in maintaining employee trust and organisational integrity. US payroll remains a highly specialised field that demands both technical expertise and regulatory awareness, making it a rewarding career for finance and HR professionals alike.
This guide explains what US payroll means, how it works, and job opportunities in this domain.
What Is the US Payroll?
US payroll refers to the complete process through which employers calculate, manage, and distribute employee compensation. It covers everything from calculating gross pay and tax withholdings to maintaining payroll records and ensuring compliance with labour and tax laws.
Payroll is not just about issuing paychecks; it also involves –
- employee classification
- benefit deductions
- record-keeping
- reporting to tax authorities.
Companies may handle payroll internally, outsource it to service providers like ADP or Paychex, or use cloud-based platforms.
According to Bill.com, payroll represents one of the largest expenses for businesses and requires close coordination between HR, finance, and compliance teams.
What Is The US Payroll Process Step By Step?
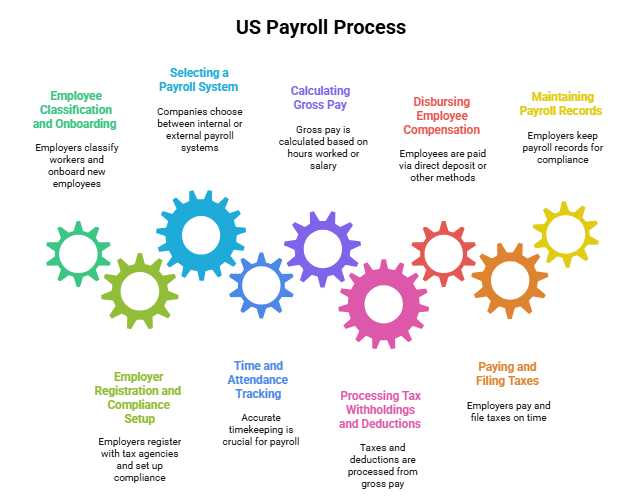
The US payroll process is structured and regulated. Each step must be executed correctly to ensure legal compliance and employee satisfaction.
Payroll typically unfolds in three stages:
- Data Collection & Setup: establishing employer accounts, classifying workers, and collecting tax forms.
- Calculation: determining gross pay, deductions, and employer contributions.
- Disbursement & Reporting: paying employees, filing taxes, and maintaining records.
1. Employee Classification and Onboarding
Employers must correctly classify workers as employees or independent contractors. This determines tax withholdings, benefits eligibility, and reporting obligations.
Employees complete forms such as:
- Form W-4: Employee’s Withholding Certificate
- Form I-9: Employment Eligibility Verification
- State-specific tax forms
Incorrect classification can result in penalties from the IRS.
2. Employer Registration and Compliance Setup
Before running payroll, employers must:
- Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS.
- Register with state tax and unemployment insurance agencies.
These registrations ensure the company can legally withhold and pay taxes on behalf of employees.
3. Selecting a Payroll System
Companies choose between internal payroll software or external payroll vendors.
Key considerations include:
- Automation of tax payments
- Integration with HR and accounting systems
- Ability to handle multi-state compliance
Popular software includes ADP, Paychex, and Workday.
4. Time and Attendance Tracking
Accurate timekeeping is crucial. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) mandates proper tracking of work hours, overtime, and breaks. Many companies use digital time-tracking systems linked to payroll software to minimise manual errors.
5. Calculating Gross Pay
Gross pay represents the total earnings before deductions.
For hourly workers:
Gross Pay = Hourly Rate × Hours Worked
For salaried employees, annual pay is divided by the number of pay periods.
Gross pay includes:
- Basic salary
- Overtime pay
- Bonuses and commissions
- Paid leaves (vacation/sick)
6. Processing Tax Withholdings and Deductions
Payroll involves several mandatory and voluntary deductions.
| Type of Deduction | Examples | Who Pays |
| Federal Income Tax | Based on Form W-4 | Employee |
| FICA Taxes | Social Security (6.2%) + Medicare (1.45%) | Shared (Employer & Employee) |
| State/Local Taxes | Based on residence or work state | Employee |
| 401(k), Insurance | Voluntary deductions | Employee |
| Garnishments | Child support, court-ordered | Employee |
For high earners (above $200,000 annually), an additional 0.9% Medicare surtax applies.
Learn more about FICA taxes from TurboTax.
7. Disbursing Employee Compensation
Employees are typically paid via:
- Direct deposit (fastest and most secure)
- Paper cheque
- Pay card
Each pay stub must display gross pay, deductions, and net pay for transparency.
8. Paying and Filing Taxes
Employers are required to deposit and file taxes on specific schedules.
Key filings include:
- Form 941: Quarterly federal tax return
- Form 940: Annual unemployment tax return
- Form W-2: Employee wage and tax statement
- Form 1099: Contractor payments
Missing deadlines can result in severe penalties. Reliable guidance is available on the IRS website.
9. Maintaining Payroll Records
Employers are required to maintain records (employee info, hours, pay rates, deductions, filings) for at least three years. Proper documentation protects companies during audits and ensures compliance.
Common documents include:
- Employee details (name, SSN, classification)
- Hours worked and pay rates
- Tax filings (Forms W-2, 941, 940)
- Benefit and deduction records
Failure to comply can result in:
- IRS penalties of 5% per month for late Form 941 filings (up to 100% of unpaid taxes)
- Back taxes and interest on underreported withholdings
- Misclassification fines of up to 100% of unpaid liabilities.
Why Understanding US Payroll Matters for Indian Professionals
For HR and finance professionals in India, working with US-based clients or companies requires a solid understanding of US payroll laws, deductions, and compliance.
It helps you:
- Handle cross-border operations
- Support global HR functions
- Improve career opportunities in multinational companies
Learning this process builds expertise that is in demand across outsourcing firms, consulting companies, and shared service centres, opening doors to the following opportunities in US Payroll.
US Payroll Jobs and Career Opportunities
Payroll careers in the US are well-paying and in demand. These roles are crucial for ensuring timely, accurate pay and compliance.
1. Payroll Specialist
A payroll specialist handles the daily payroll process, calculations, reporting, and employee queries.
Typical qualifications:
- 2+ years of payroll or HR experience
- Knowledge of payroll systems (ADP, Paychex, Workday)
- Strong attention to detail
Learn more from Indeed’s Payroll Job Guide.
2. Payroll Manager
A payroll manager oversees payroll teams, ensures compliance, and manages audits.
Core responsibilities include:
- Supervising payroll staff
- Approving payroll runs and reports
- Handling compliance across multiple states
Many employers prefer professionals with a Certified Payroll Professional (CPP) credential.
You can read detailed descriptions at 4Corner Resources.
Skills Needed for Payroll Professionals
| Technical Skills | Soft Skills |
| Payroll software (ADP, QuickBooks) | Communication |
| Knowledge of tax and compliance laws | Accuracy and detail orientation |
| Financial reporting | Problem-solving |
| Multi-state payroll handling | Confidentiality and integrity |
For those starting their career, a structured learning path through certification can fast-track growth in this field.
Conclusion: Build Your US Payroll Expertise with SkillDeck
The US payroll process combines legal compliance, accurate calculation, and efficient technology. From onboarding employees to filing taxes, each step demands precision and responsibility.
If you’re looking to build a career in US payroll management, start by learning the foundations of federal and state tax laws, payroll systems, and compliance.
SkillDeck’s US Payroll Certification Course helps you gain hands-on experience with practical simulations, updated tax laws, and compliance training, preparing you for real-world payroll roles in global organisations.
FAQs About US Payroll
1. How is US payroll different from Indian payroll?
Unlike Indian payroll, US payroll involves multiple federal and state tax systems, Social Security, Medicare, and complex benefit deductions. It also requires adherence to IRS (Internal Revenue Service) and Department of Labor (DOL) regulations.
2. What are the key components of US payroll?
The main components include gross pay, federal and state income tax, FICA taxes (Social Security and Medicare), employee benefits, and employer contributions.
3. Who manages payroll in the US?
Payroll can be managed internally by HR or accounting teams, or outsourced to payroll service providers like ADP, Gusto, or Paychex to ensure accuracy and compliance.
4. What are FICA taxes in the US payroll?
FICA (Federal Insurance Contributions Act) taxes are mandatory deductions that fund Social Security and Medicare programs. Both employers and employees contribute to these taxes.
5. How often is payroll processed in the US?
Most US employers process payroll weekly, biweekly, semimonthly, or monthly, depending on company policy and state requirements.
6. What are the major payroll taxes in the US?
The main taxes include federal income tax, state income tax (in applicable states), Social Security tax, and Medicare tax. Employers must also pay federal and state unemployment taxes.
7. What happens if payroll taxes are filed late in the US?
Late filing or non-payment of payroll taxes can lead to heavy IRS penalties, interest charges, and even legal action against the employer.
8. What software is commonly used for US payroll management?
Popular payroll tools include ADP, QuickBooks Payroll, Paychex, Gusto, and Workday. These systems help automate calculations, tax filings, and compliance tracking.
9. How Can International Professionals learn US payroll processing?
Professionals outside the US can enroll in online certification courses like SkillDeck’s US Payroll Certification Course, which provides in-depth training on payroll laws, calculations, and compliance procedures.
